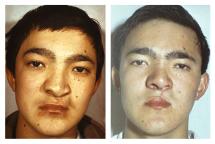
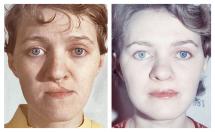
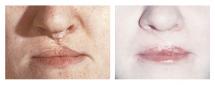
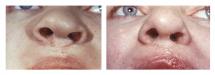
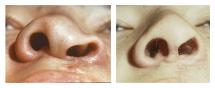
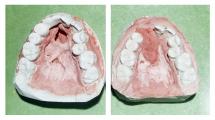
Reconstructive surgeries are used to restore the forms and functions of the face and body.
Reconstructive surgeries are carried out on the skin, muscles, fascial and bone tissues, as well as on arteries.
Reconstructive operations are conducted in cases of:
1) congenital diseases -
- hypoplasia of the zygomatic, frontal and orbital areas,
- cleft lip, palate and face,
- asymmetry of the jaws,
- atrophy of the muscle tissue of face and body,
- lipodystrophy,
2) posttraumatic defects and deformations of soft and bone tissues of the face and body,
3) cancerous neoplasms of the face and body.
Reconstructive surgeries are complex and multi-step procedures. The aim of these operations is the substitution of tissue defects, the removal of deformities and the restoration of disrupted functions.
Various techniques are applied using local, musculocutaneous and muscle-fascial flaps, free skin and bone grafts.
Depending on the case, silicone implants are used simultaneously for attainment of optimal contours of the face and body.
Microsurgical techniques are applied while using complex muscle flaps. These operations are often conducted by a team of plastic surgeons.
Age: from infants to 75 years of age.
Anaesthesia: general anaesthetic.
Duration of operation: 1-10 hours.
Postoperative recovery:
- Patient needs a long stay in hospital 1-4 weeks.
- Dynamic observation from daily to monthly evaluations, until the next phase of the treatment.
- Recovery can take from 10 days to 2-3 months.
Cost: the cost of these procedures is quite high and is usually paid by insurance.
What is important to consider?
- The patient needs to quit smoking several months prior to the operation.
- It is important to correctly identify the phases involved in these operations.
- These operations must be carried out by a plastic-reconstructive surgeon with extensive skills and experience - and one who has an outstanding command of microsurgical techniques.